Muslim-American Terrorism
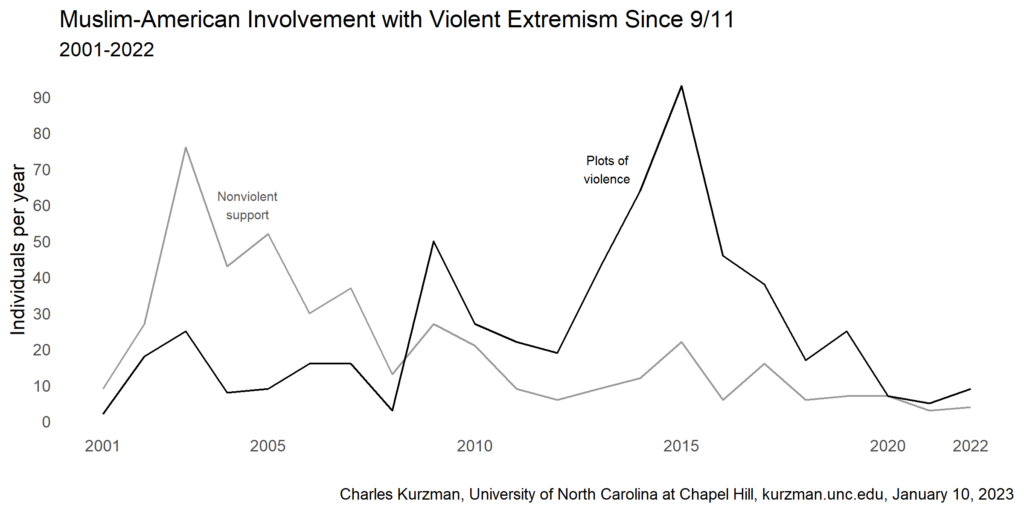
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2023
Examine the data for yourself here. A full collection of past reports is available here.
Fatalities in the U.S. from Muslim-American involvement with violent extremism since 9/11: 145.
Victims of murder in the U.S. since 9/11, according to the FBI’s Expanded Homicide Offense Counts: 312,317.
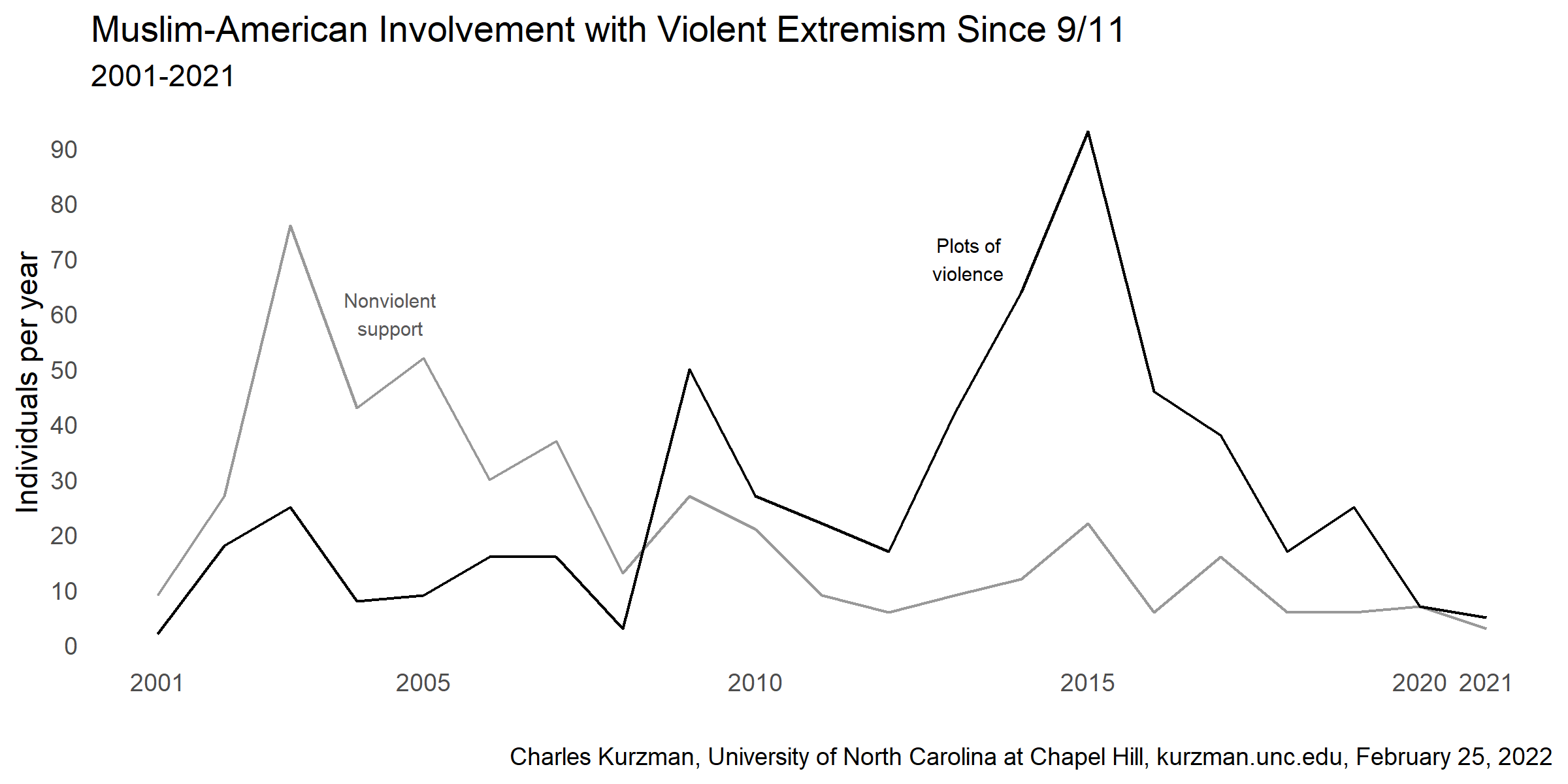
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2022
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2021
I’m Sorry I Called You a Terrorist
 Charles Kurzman, “I’m Sorry I Called You a Terrorist,” October 29, 2021. Just before the pandemic, a young woman came to my office and asked what I knew about her father. “Is my father a terrorist?” More…
Charles Kurzman, “I’m Sorry I Called You a Terrorist,” October 29, 2021. Just before the pandemic, a young woman came to my office and asked what I knew about her father. “Is my father a terrorist?” More…
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2020
 Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2020,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 14, 2021. Seven Muslim-Americans were arrested or killed during alleged involvement with violent extremism in 2020, the lowest total since 2008. This continues the decline since the peak of 90 cases in 2015. Islamic extremism played almost no role in the considerable unrest that the United States experienced in 2020. The total number of fatalities in the United States from Muslim-American violent extremism since 9/11 remained at 141. Over this same period, there have been more than 309,000 murders in the United States. More…
Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2020,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 14, 2021. Seven Muslim-Americans were arrested or killed during alleged involvement with violent extremism in 2020, the lowest total since 2008. This continues the decline since the peak of 90 cases in 2015. Islamic extremism played almost no role in the considerable unrest that the United States experienced in 2020. The total number of fatalities in the United States from Muslim-American violent extremism since 9/11 remained at 141. Over this same period, there have been more than 309,000 murders in the United States. More…
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2019
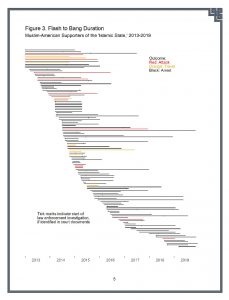
 Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2019,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 21, 2020. Twenty-four Muslim-Americans were arrested for alleged involvement with violent extremism in 2019, higher than the previous year but lower than the peak years of 2014-2016. This year’s annual report also presents new data on the lengthening period between radicalization and attempts at violence, allaying concerns voiced by counterterrorism officials about a quickening pace of ‘flash’ to ‘bang.'” More…
Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2019,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 21, 2020. Twenty-four Muslim-Americans were arrested for alleged involvement with violent extremism in 2019, higher than the previous year but lower than the peak years of 2014-2016. This year’s annual report also presents new data on the lengthening period between radicalization and attempts at violence, allaying concerns voiced by counterterrorism officials about a quickening pace of ‘flash’ to ‘bang.'” More…
The Privacy Rights of Terrorism Defendants, Muslim and Non-Muslim
 Charles Kurzman, “The Privacy Rights of Terrorism Defendants, Muslim and Non-Muslim,” Lawfare, April 5, 2019. The official position of the Department of Justice—according to a legal brief filed in February—is that association with a terrorism charge is so stigmatizing that defendants should not be publicly identified. This is puzzling, since the department itself periodically releases a list of Muslim Americans convicted in terrorism-related cases, as well as hundreds of press releases naming Muslim American terrorism defendants. Yet the department has never released a list of domestic terrorism-related cases, and its press releases named only one-quarter of defendants involved in right-wing violent extremism. More…
Charles Kurzman, “The Privacy Rights of Terrorism Defendants, Muslim and Non-Muslim,” Lawfare, April 5, 2019. The official position of the Department of Justice—according to a legal brief filed in February—is that association with a terrorism charge is so stigmatizing that defendants should not be publicly identified. This is puzzling, since the department itself periodically releases a list of Muslim Americans convicted in terrorism-related cases, as well as hundreds of press releases naming Muslim American terrorism defendants. Yet the department has never released a list of domestic terrorism-related cases, and its press releases named only one-quarter of defendants involved in right-wing violent extremism. More…
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2018
 Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2018,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 22, 2019. The wave of Muslim-Americans associating themselves with the self-proclaimed “Islamic State” appears to have dwindled, continuing a downward trend that was visible in the final year of the Obama administration. There were no incidents or arrests in 2018 involving Muslim extremists who entered the United States illegally. These findings contradict the alarms about terrorism sounded by the Trump administration. In a survey conducted for this report, terrorism experts attribute the decline in Muslim-American involvement with violent extremism to the loss of territory by the Islamic State, the reduction in online recruitment, and the already small scale of Muslim-American extremism. More…
Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2001-2018,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 22, 2019. The wave of Muslim-Americans associating themselves with the self-proclaimed “Islamic State” appears to have dwindled, continuing a downward trend that was visible in the final year of the Obama administration. There were no incidents or arrests in 2018 involving Muslim extremists who entered the United States illegally. These findings contradict the alarms about terrorism sounded by the Trump administration. In a survey conducted for this report, terrorism experts attribute the decline in Muslim-American involvement with violent extremism to the loss of territory by the Islamic State, the reduction in online recruitment, and the already small scale of Muslim-American extremism. More…
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2017
 Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2017,” January 18, 2018. The number of Muslim-Americans associated with violent extremism continued a downward trend that was visible in the final year of the Obama administration. This trend defied expectations that President Donald Trump’s presidency would generate a distinctive pattern of violent extremism. The administration did not identify “support networks” for terrorism in the United States, as Trump had promised, and Trump’s anti-Muslim rhetoric and policies did not trigger a backlash of increased violent extremism, as some Muslim extremists had predicted. More…
Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2017,” January 18, 2018. The number of Muslim-Americans associated with violent extremism continued a downward trend that was visible in the final year of the Obama administration. This trend defied expectations that President Donald Trump’s presidency would generate a distinctive pattern of violent extremism. The administration did not identify “support networks” for terrorism in the United States, as Trump had promised, and Trump’s anti-Muslim rhetoric and policies did not trigger a backlash of increased violent extremism, as some Muslim extremists had predicted. More…
Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2016
 Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2016,” January 26, 2017. The number of Muslim-Americans associated with violent extremism dropped 40 percent in 2016, as compared with the previous year, although this drop was overshadowed by the mass shooting in Orlando, Florida, in June 2016. Only 20 percent of these individuals had family backgrounds in one of the seven Muslim-majority countries reportedly designated for immigrant bans by the Trump administration. There have been no fatalities in the U.S. since 9/11 caused by extremists from these countries. More…
Charles Kurzman, “Muslim-American Involvement with Violent Extremism, 2016,” January 26, 2017. The number of Muslim-Americans associated with violent extremism dropped 40 percent in 2016, as compared with the previous year, although this drop was overshadowed by the mass shooting in Orlando, Florida, in June 2016. Only 20 percent of these individuals had family backgrounds in one of the seven Muslim-majority countries reportedly designated for immigrant bans by the Trump administration. There have been no fatalities in the U.S. since 9/11 caused by extremists from these countries. More…
Charles Kurzman, “These Numbers Show Why Trump’s Muslim Entry Limit Is Absurd,” Huffington Post, January 26, 2017.
Coverage by National Public Radio, January 27, 2017; The New York Times, January 28, 2017; The Washington Post, January 28, 2017; The Washington Post, February 7, 2017; The Wall Street Journal, February 10, 2017.
In 2016, Americans were less likely to be killed by Muslim extremists (1 in six million) than for being Muslim (one in one million): 54 fatalities in a population of approximately 324 million vs. 4 fatalities (Khalid Jabara in Tulsa and Imam Maulama Akonjee, Thara Uddin, and Nazma Khanam in New York) in a population of approximately 3 million. Update of 2015 data; coverage by Nicholas Kristof, The New York Times, February 12, 2017.
Terrorism Frightens Us ‘Far Out of Proportion’ to Actual Risk
 Greg Toppo, “Expert: Terrorism Frightens Us ‘Far Out of Proportion’ to Actual Risk,” USA Today, September 21, 2016 (paper edition, September 22, 2016). “Q: In 2016, how likely is it that an American will be killed by a terrorist, Muslim or non-Muslim? A: Fortunately, terrorism has been very rare in the United States. … Terrorism frightens people far out of proportion to the actual number of victims — indeed, that is its primary goal: to create a sense of terror.” More….
Greg Toppo, “Expert: Terrorism Frightens Us ‘Far Out of Proportion’ to Actual Risk,” USA Today, September 21, 2016 (paper edition, September 22, 2016). “Q: In 2016, how likely is it that an American will be killed by a terrorist, Muslim or non-Muslim? A: Fortunately, terrorism has been very rare in the United States. … Terrorism frightens people far out of proportion to the actual number of victims — indeed, that is its primary goal: to create a sense of terror.” More….
Also: interview with Michel Martin on The Diane Rehm Show, National Public Radio, September 20, 2016.
The Police Chief: Research in Brief
 David Schanzer, Charles Kurzman, Jessica Toliver, and Elizabeth Miller, “Research in Brief: The Challenge and Promise of Using Community Policing Strategies to Prevent Violent Extremism,” The Police Chief (International Association of Chiefs of Police), July 2016, pp. 14-15. “Five years ago, the White House issued a strategy calling for the development of partnerships between police and communities as the key element of an effort to counter violent extremism (CVE) in the United States. The authors’ research assesses the challenges and promise of this strategy, based on a survey of U.S. law enforcement agencies and hundreds of hours of interviews and site visits with police departments and community members.” More…
David Schanzer, Charles Kurzman, Jessica Toliver, and Elizabeth Miller, “Research in Brief: The Challenge and Promise of Using Community Policing Strategies to Prevent Violent Extremism,” The Police Chief (International Association of Chiefs of Police), July 2016, pp. 14-15. “Five years ago, the White House issued a strategy calling for the development of partnerships between police and communities as the key element of an effort to counter violent extremism (CVE) in the United States. The authors’ research assesses the challenges and promise of this strategy, based on a survey of U.S. law enforcement agencies and hundreds of hours of interviews and site visits with police departments and community members.” More…
Well Said: America and Terrorism
 Charles Kurzman, “America and Terrorism,” interview with Brandon Bieltz on UNC-Chapel Hill’s Well Said podcast, April 27, 2016. In this week’s episode of the Well Said podcast, sociology professor Charles Kurzman discusses terrorism and his research on the small number of Muslim-Americans who join militant groups. More…
Charles Kurzman, “America and Terrorism,” interview with Brandon Bieltz on UNC-Chapel Hill’s Well Said podcast, April 27, 2016. In this week’s episode of the Well Said podcast, sociology professor Charles Kurzman discusses terrorism and his research on the small number of Muslim-Americans who join militant groups. More…
Community Policing to Prevent Violent Extremism
 David Schanzer, Charles Kurzman, Jessica Toliver, and Elizabeth Miller, “The Challenge and Promise of Using Community Policing Strategies to Prevent Violent Extremism,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 2016. “Policing agencies face multiple obstacles to creating community partnerships focused on preventing acts of violent extremism. But … some policing agencies are following a set of promising practices which, if applied effectively, can result in increasing trust between the police and the communities they serve. These trusting relationships can serve as a platform for addressing many public safety threats, including, but not limited to, violent extremism.” More…
David Schanzer, Charles Kurzman, Jessica Toliver, and Elizabeth Miller, “The Challenge and Promise of Using Community Policing Strategies to Prevent Violent Extremism,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, January 2016. “Policing agencies face multiple obstacles to creating community partnerships focused on preventing acts of violent extremism. But … some policing agencies are following a set of promising practices which, if applied effectively, can result in increasing trust between the police and the communities they serve. These trusting relationships can serve as a platform for addressing many public safety threats, including, but not limited to, violent extremism.” More…
America Is Holding Itself Hostage to Terrorism
 Charles Kurzman, “America Is Holding Itself Hostage to Terrorism,” The Huffington Post, December 17, 2015. “So far this year, Americans have been more likely to be killed for being Muslim — than by a Muslim. One in one million Muslim Americans died because of hatred for their faith, compared with one in 17 million other Americans who died at the hands of Muslim militants. Fortunately, both types of violence are incredibly rare. … We need to stop holding ourselves hostage to rare incidents of Islamic violence. We can only remain the land of the free if we start behaving like the home of the brave.” More…
Charles Kurzman, “America Is Holding Itself Hostage to Terrorism,” The Huffington Post, December 17, 2015. “So far this year, Americans have been more likely to be killed for being Muslim — than by a Muslim. One in one million Muslim Americans died because of hatred for their faith, compared with one in 17 million other Americans who died at the hands of Muslim militants. Fortunately, both types of violence are incredibly rare. … We need to stop holding ourselves hostage to rare incidents of Islamic violence. We can only remain the land of the free if we start behaving like the home of the brave.” More…
Ideological Violence Is Terrorism
 Charles Kurzman, “Ideological Violence Is Terrorism,” New York Times “Room for Debate” forum, December 3, 2015. “Violence like the shooting in San Bernardino, Calif., raises an existential question: What are we most afraid of? Ideological killings, which occur relatively rarely, or “ordinary” violence — including school shootings, gang murders, domestic abuse and other forms of homicide — which is much more common?” More…
Charles Kurzman, “Ideological Violence Is Terrorism,” New York Times “Room for Debate” forum, December 3, 2015. “Violence like the shooting in San Bernardino, Calif., raises an existential question: What are we most afraid of? Ideological killings, which occur relatively rarely, or “ordinary” violence — including school shootings, gang murders, domestic abuse and other forms of homicide — which is much more common?” More…
A Resolute Commitment to Coexistence — Now That Projects Strength
![]() Charles Kurzman, “A Resolute Commitment to Coexistence — Now That Projects Strength,” IslamiCommentary, November 30, 2015. “Over the past year, the Islamic State came to realize that even small-scale, low-tech attacks by Muslim extremists — a knifing in Boston, rifle shots in Chattanooga — could attract massive attention and concern. Few Muslims have taken up the call to mayhem, but a few is enough. Opportunistic politicians will do the Islamic State’s work for it, warning their constituencies that they face an existential threat from ISIS and its supporters. Claiming to project strength, these politicians stoke the sense of vulnerability that the Islamic State aims to instill.” More…
Charles Kurzman, “A Resolute Commitment to Coexistence — Now That Projects Strength,” IslamiCommentary, November 30, 2015. “Over the past year, the Islamic State came to realize that even small-scale, low-tech attacks by Muslim extremists — a knifing in Boston, rifle shots in Chattanooga — could attract massive attention and concern. Few Muslims have taken up the call to mayhem, but a few is enough. Opportunistic politicians will do the Islamic State’s work for it, warning their constituencies that they face an existential threat from ISIS and its supporters. Claiming to project strength, these politicians stoke the sense of vulnerability that the Islamic State aims to instill.” More…
Why We Care About Some Gunmen, and Not Others
 Charles Kurzman, “Why We Care About Some Gunmen, and Not Others,” IslamiCommentary, August 31, 2015. Not every gunshot echoes alike. Some echoes fade quickly, and are only heard in a single neighborhood. Others resonate nationwide, making headlines for days or weeks, like Vester Flanagan’s murder of two television journalists near Roanoke, Virginia, last week — one of a series of shooters to gain national attention over the past year, including Mohammad Abdulazeez in Chattanooga, Tennessee; Dylann Roof in Charleston, South Carolina; and Darren Wilson in Ferguson, Missouri. These are not names that you would ordinarily see grouped together, and they do not have anything in common, except that they are American males who used lethal gunfire to address their personal sense of threat — and then became household names. Beyond the horrific nature of the crimes, what keeps these particular gunmen in the news is their adoption by political movements as symbols of a broader threat. More…
Charles Kurzman, “Why We Care About Some Gunmen, and Not Others,” IslamiCommentary, August 31, 2015. Not every gunshot echoes alike. Some echoes fade quickly, and are only heard in a single neighborhood. Others resonate nationwide, making headlines for days or weeks, like Vester Flanagan’s murder of two television journalists near Roanoke, Virginia, last week — one of a series of shooters to gain national attention over the past year, including Mohammad Abdulazeez in Chattanooga, Tennessee; Dylann Roof in Charleston, South Carolina; and Darren Wilson in Ferguson, Missouri. These are not names that you would ordinarily see grouped together, and they do not have anything in common, except that they are American males who used lethal gunfire to address their personal sense of threat — and then became household names. Beyond the horrific nature of the crimes, what keeps these particular gunmen in the news is their adoption by political movements as symbols of a broader threat. More…
The Other Terror Threat
 Charles Kurzman and David Schanzer, “The Other Terror Threat,” The New York Times, June 16, 2015. “If you keep up with the news, you know that a small but steady stream of American Muslims, radicalized by overseas extremists, are engaging in violence here in the United States. But headlines can mislead. The main terrorist threat in the United States is not from violent Muslim extremists, but from right-wing extremists. Just ask the police. In a survey we conducted with the Police Executive Research Forum last year of 382 law enforcement agencies, 74 percent reported anti-government extremism as one of the top three terrorist threats in their jurisdiction; 39 percent listed extremism connected with Al Qaeda or like-minded terrorist organizations.” More…
Charles Kurzman and David Schanzer, “The Other Terror Threat,” The New York Times, June 16, 2015. “If you keep up with the news, you know that a small but steady stream of American Muslims, radicalized by overseas extremists, are engaging in violence here in the United States. But headlines can mislead. The main terrorist threat in the United States is not from violent Muslim extremists, but from right-wing extremists. Just ask the police. In a survey we conducted with the Police Executive Research Forum last year of 382 law enforcement agencies, 74 percent reported anti-government extremism as one of the top three terrorist threats in their jurisdiction; 39 percent listed extremism connected with Al Qaeda or like-minded terrorist organizations.” More…
- A more detailed report of this article’s findings is available in Charles Kurzman and David Schanzer, “Law Enforcement Assessment of the Violent Extremism Threat,” Triangle Center on Terrorism and Homeland Security, June 25, 2015.
The PATRIOT Act Can’t Keep America Safe from Right-Wing Violence
 Charles Kurzman, “The PATRIOT Act Can’t Keep America Safe from Right-Wing Violence,” IslamiCommentary, May 27, 2015. With the “USA PATRIOT Act” set to expire at the end of the month, you might expect supporters of domestic surveillance to tout the take-down of the biggest plot of violent extremism America has experienced so far this year: an attempt to destroy an entire American community. But the plot was disrupted using standard investigative tools, not PATRIOT Act surveillance. That’s because the most powerful portion of the PATRIOT Act, Section 215, is limited to investigations of “international terrorism,” while this plot was a case of domestic terrorism. More…
Charles Kurzman, “The PATRIOT Act Can’t Keep America Safe from Right-Wing Violence,” IslamiCommentary, May 27, 2015. With the “USA PATRIOT Act” set to expire at the end of the month, you might expect supporters of domestic surveillance to tout the take-down of the biggest plot of violent extremism America has experienced so far this year: an attempt to destroy an entire American community. But the plot was disrupted using standard investigative tools, not PATRIOT Act surveillance. That’s because the most powerful portion of the PATRIOT Act, Section 215, is limited to investigations of “international terrorism,” while this plot was a case of domestic terrorism. More…
Homegrown Terrorism Threat Was Overhyped
 David Schanzer and Charles Kurzman, “Homegrown Terrorism Threat Was Overhyped,” Newark Star-Ledger, April 14, 2014. In the aftermath of the Boston Marathon bombing one year ago, many commentators and public officials called this tragedy a harbinger of more homegrown terrorist attacks to come. Fortunately, no one has been killed by homegrown terrorists in the past year and there have been no copycat attacks. A nationwide survey of law enforcement agencies we are conducting in collaboration with the Police Executive Research Forum shows that more than half of the agencies report little or no threat from al Qaeda-inspired extremism. Only 2 percent report the threat as “severe.” More…
David Schanzer and Charles Kurzman, “Homegrown Terrorism Threat Was Overhyped,” Newark Star-Ledger, April 14, 2014. In the aftermath of the Boston Marathon bombing one year ago, many commentators and public officials called this tragedy a harbinger of more homegrown terrorist attacks to come. Fortunately, no one has been killed by homegrown terrorists in the past year and there have been no copycat attacks. A nationwide survey of law enforcement agencies we are conducting in collaboration with the Police Executive Research Forum shows that more than half of the agencies report little or no threat from al Qaeda-inspired extremism. Only 2 percent report the threat as “severe.” More…
Muslim American Terrorism Since 9/11: Why So Rare?
Charles Kurzman, David Schanzer, and Ebrahim Moosa, “Muslim American Terrorism Since 9/11: Why So Rare?” The Muslim World, July 2011, pages 464–483: “Terrorist front organizations and their multicultural enablers claim that the threat of Islamic terrorism is exaggerated. Right-wing Islamophobes claim that the threat of Islamic terrorism is not being taken seriously enough. So which is it? In order to bring evidence to bear on this vexatious issue, we have attempted to gather information on every Muslim-American terrorism suspect and perpetrator since September 11, 2011.” More…
Anti-Terror Lessons of Muslim-Americans
David Schanzer, Charles Kurzman, and Ebrahim Moosa, “Anti-Terror Lessons of Muslim-Americans,” Report for the National Institute of Justice, January 6, 2010.